The concept of Extended Reality, or XR, arises from the belief that a new technological leap is still needed to reach the maximum potential of Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR).
This technological leap would allow the creation of higher quality and more realistic XR experiences, getting much closer to the experiences that we can live and perceive in the real world.
We can take the example of Augmented Reality, which in the case of inserting 3D objects that do not cast shadows, would cause an unreal perception by the user to feel it as a "fake" environment.
For this reason, technological advances in Extended Reality will gradually allow us to develop increasingly realistic XR experiences, which will finally break down the line between distinguishing the real and the virtual.
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
Extended Reality is a combination of the so-called immersive technologies: VR (Virtual Reality) + AR (Augmented Reality) + MR (Mixed Reality). In other words, Extended Reality, or XR, encompasses all environments, real and virtual, represented by computer graphics or mobile devices.
The X in X-Reality can represent any letter: V virtual reality, A augmented reality, M mixed reality. To understand extended reality you first have to understand the rest of the realities.
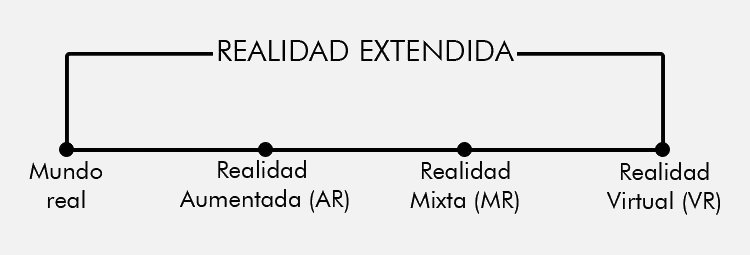
In order to get all the realities grouped in a single box and for the person to have a simultaneous VR, AR and MR experience it is still necessary to solve certain technical issues related to aspects such as lighting, motion tracking, etc.
Extended Reality advances are directed in this direction, trying to combine physical and virtual realities until the user is not able to distinguish between them, creating an Extended Reality within the reach of anyone and improving our lives, providing experiences that so far seem like science fiction.
But in reality, it is not a science fiction far removed from our present, since there are several technology companies that are participating in the race to achieve a complete XR experience, and that may be able to achieve it in a matter of years. We can talk about companies such as: Unity Technologies, Qualcomm, Oculus, Nvidia or Steam, among others.
Next we will briefly define and detail each of the technologies that currently make up Extended Reality, so that you have a brief brushstroke of each of them and can distinguish them without excessive problems.
What is Virtual Reality (VR)?
Virtual reality is a concept with which many of us are familiar. It is not a new technology, it has been worked with since 1968, although its democratization did not occur until 2013 with the birth of the Oculus Rift DK1.
Virtual reality is a computer-generated representation of a virtual world. In order to enjoy these experiences it is necessary to use VR glasses, helmets... (HMD).
It may be believed that the application of this technology is only intended for entertainment and more specifically for playing video games, but as we demonstrate in DeuSens, it can have multiple applications in business and the corporate world, giving a very clear example with our project HMY Innovation Paradigm.
If you are interested in discovering more uses of Virtual Reality for companies that can inspire you for your next project, we recommend reading our post that will let you know more in detail all the possibilities of VR and how to apply it successfully in your company.
Virtual Reality success stories for companies
What is augmented reality (AR)?
Augmented reality (AR) consists of a technology whose purpose is to achieve an enrichment of the real world through the introduction of virtual elements. These virtual elements are superimposed on the real space, and to do so augmented reality requires a camera that captures the real environment, and a processor that is capable of generating such virtual content.
That is, with augmented reality virtual content is generated and then inserted into the real world. For this reason, to live an AR experience it is necessary to have a device that is capable of carrying out these two functions such as a smartphone, a tablet, augmented reality glasses, a computer, etc.
One of the main features that differentiates augmented reality from virtual reality is that the person experiencing the AR experience is fully aware of their real environment and is able to interact with both realities simultaneously.
AR can be a very useful tool in day-to-day life. At DeuSens we make use of this technology to apply it for example in the industrial sector as in this project: HIAB: augmented reality for industrial catalogs.
If you want to know more ways to apply Augmented Reality in companies of all kinds of sectors, we recommend you to read our post with examples of use so you can see for yourself all the possibilities that this technology has.
Examples of Augmented Reality use for companies
What is mixed reality (MR)?
In 1994, Professor Paul Migram and Fumio Kishino created the concept of mixed reality to explain the relationship between VR and AR.
Mixed reality is a combination of VR and AR that brings together the best aspects of each, unifying the experience.
On the one hand, it allows you to see the real world, as happens with augmented reality, and on the other hand, it has the potential to create incredible virtual worlds, typical of virtual reality. This is not all, since MR anchors these objects to a point in real space, in order to make them seem more real.
Mixed Reality not only facilitates user interaction with the virtual environment but also allows physical objects in the real environment surrounding the user to serve as elements of interaction with the virtual environment.
At DeuSens we have used this technology for this Acciona project, in which operators used Hololens Mixed Reality glasses to streamline the maintenance process of a water pump and avoid errors, seeing the steps to be performed on a virtual water pump in real time.
Extended Reality uses in different sectors
From military applications to retail innovations, XR is not only enhancing traditional methods, but also opening doors to new possibilities in fields such as healthcare, education, and engineering.
Below, we explore how Extended Reality is being implemented in a variety of professional fields, demonstrating its value and versatility in a variety of practical applications. Through Extended Reality, we discover unlimited potential for learning, operational efficiency, and greater human connection in an ever-evolving technological landscape.
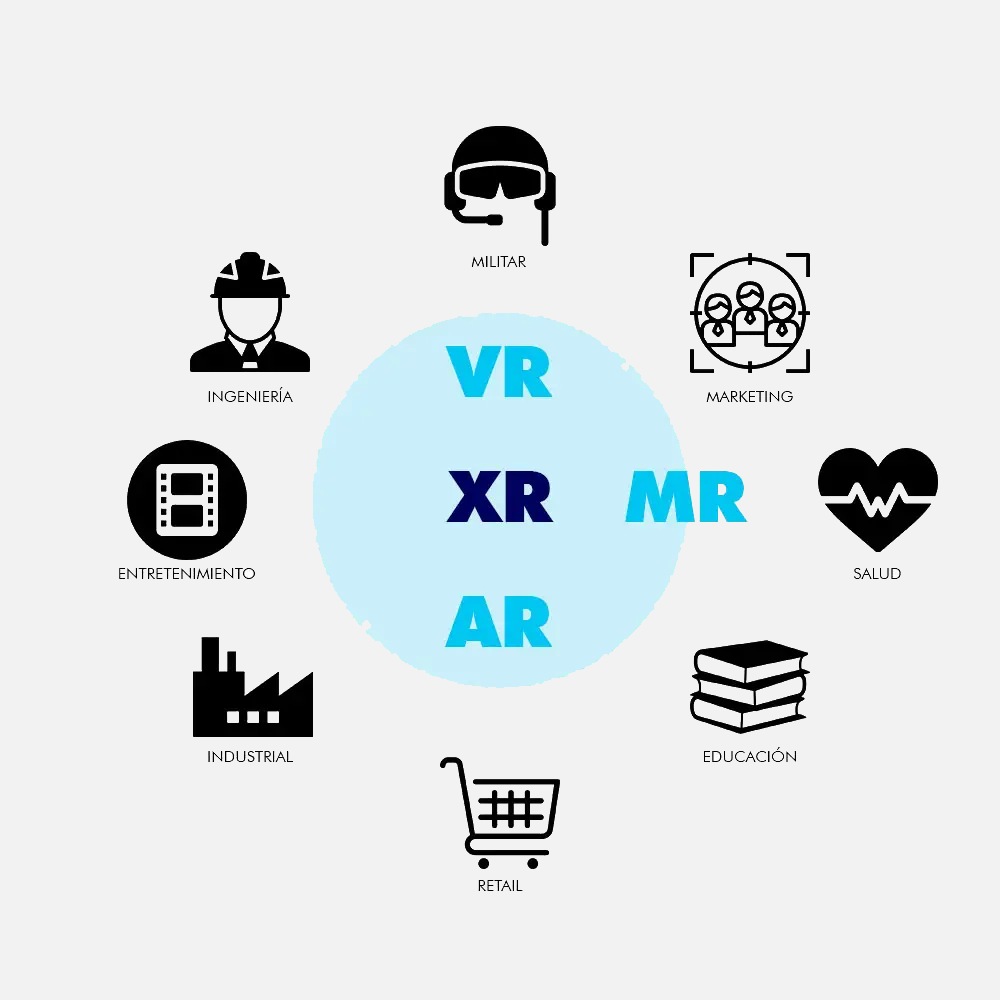
1. Extended Reality in the Military
Extended Reality (XR) is revolutionizing military training with advanced simulations and training programs that recreate realistic combat scenarios. These XR systems allow soldiers to gain experience in a controlled environment, minimizing real-world risks and improving tactical effectiveness in the field.


2. Marketing & Extended Reality
Marketing is transformed with the implementation of Extended Reality. Campaigns incorporating XR provide highly immersive brand experiences, allowing consumers to interact with products virtually prior to purchase, enriching the customer's decision and enhancing brand image.
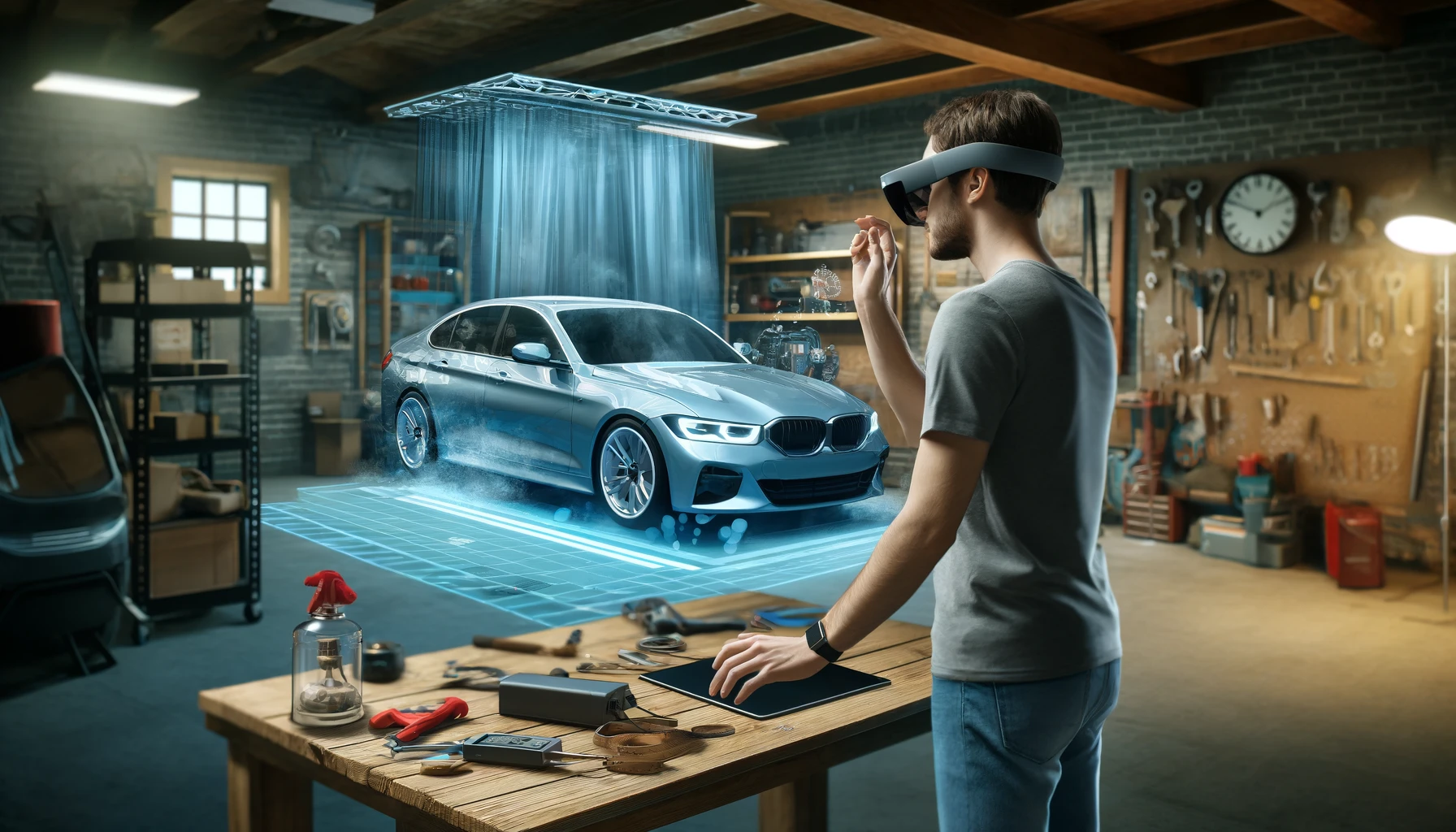
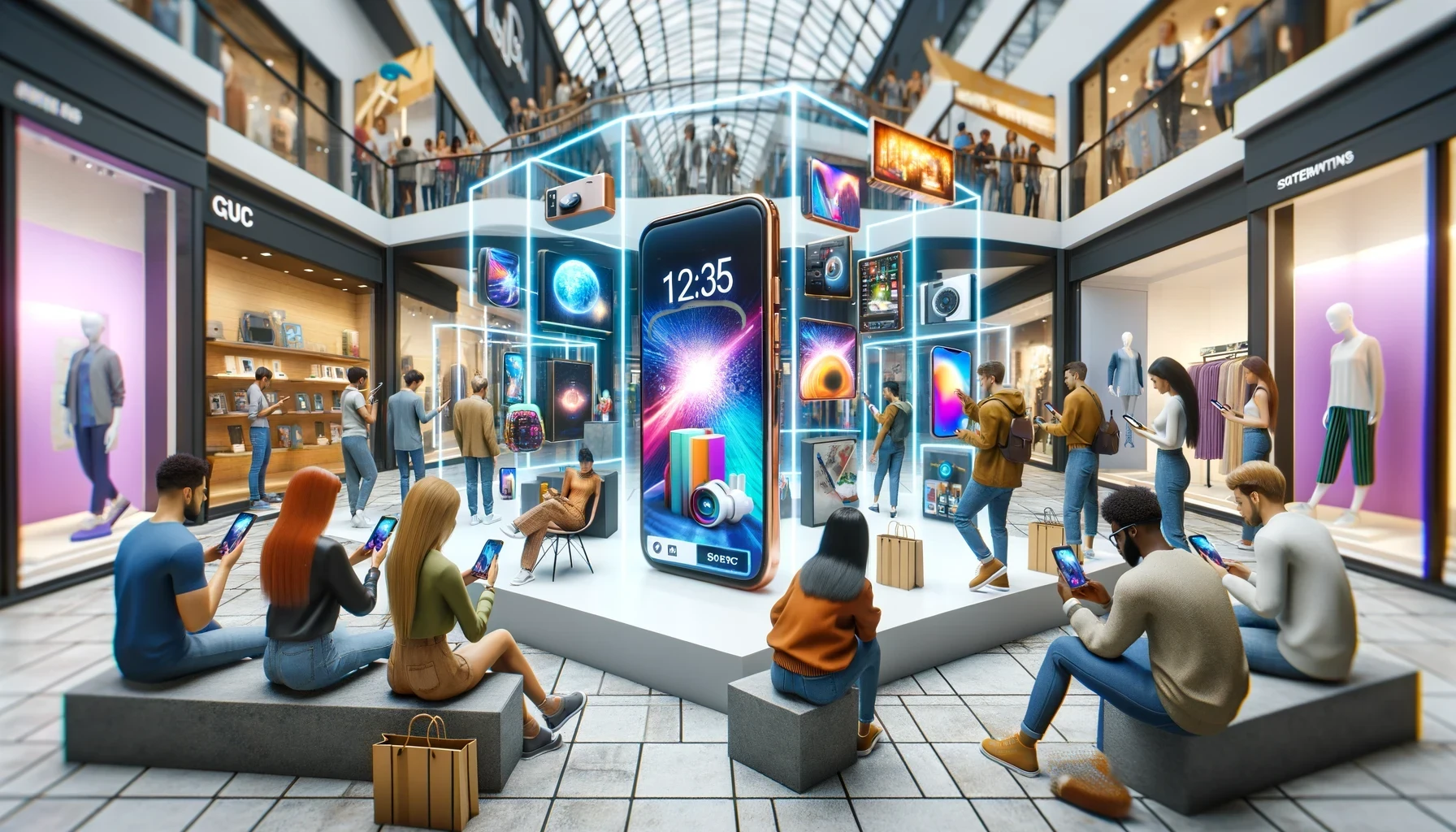


3. Enhanced health through Extended Reality
In the healthcare sector, XR is used to improve medical training, surgical interventions and rehabilitation therapies. The application of XR technologies in complex medical procedures enables healthcare professionals to practice without risk, contributing to safer and more efficient patient care.
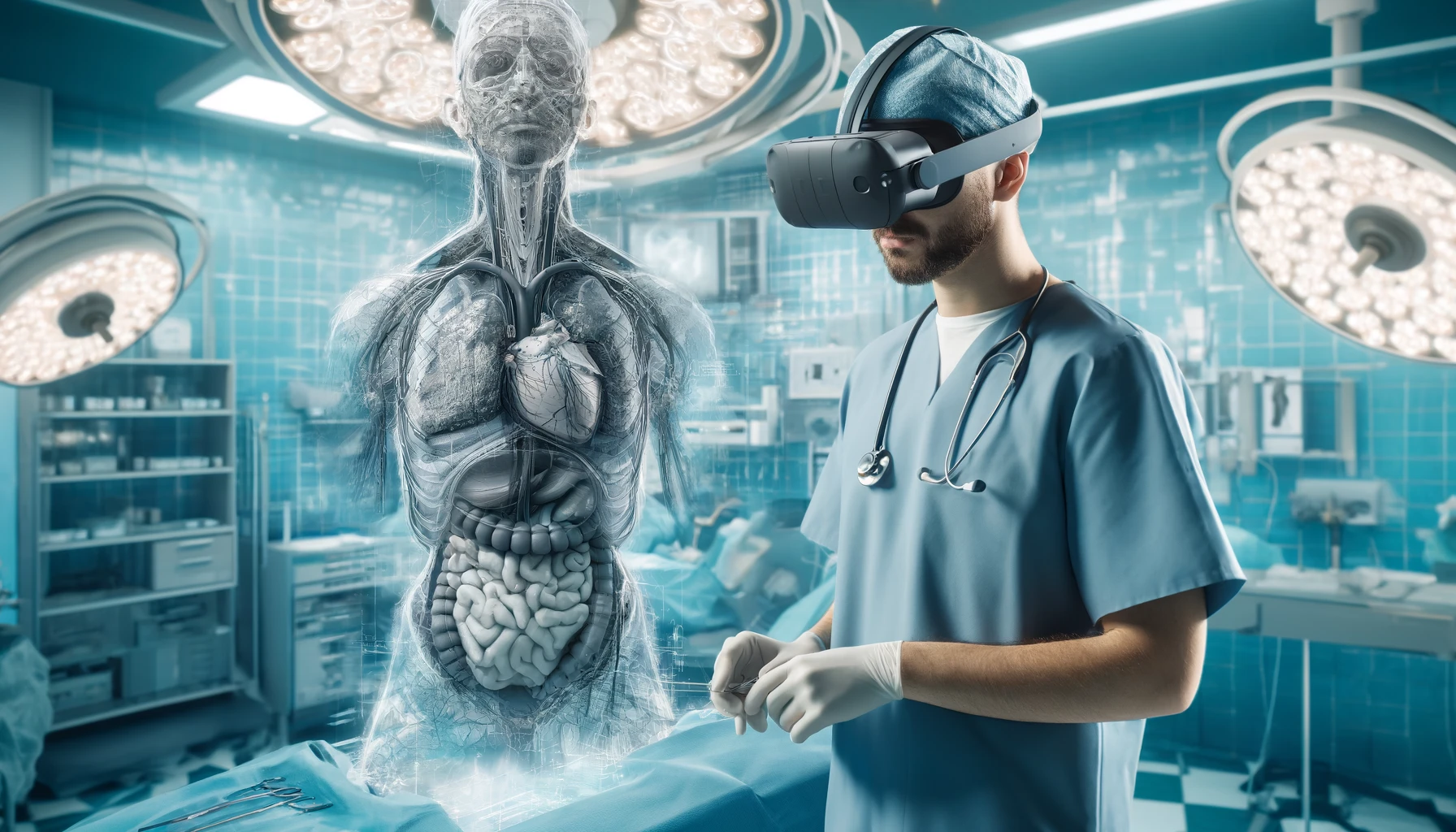
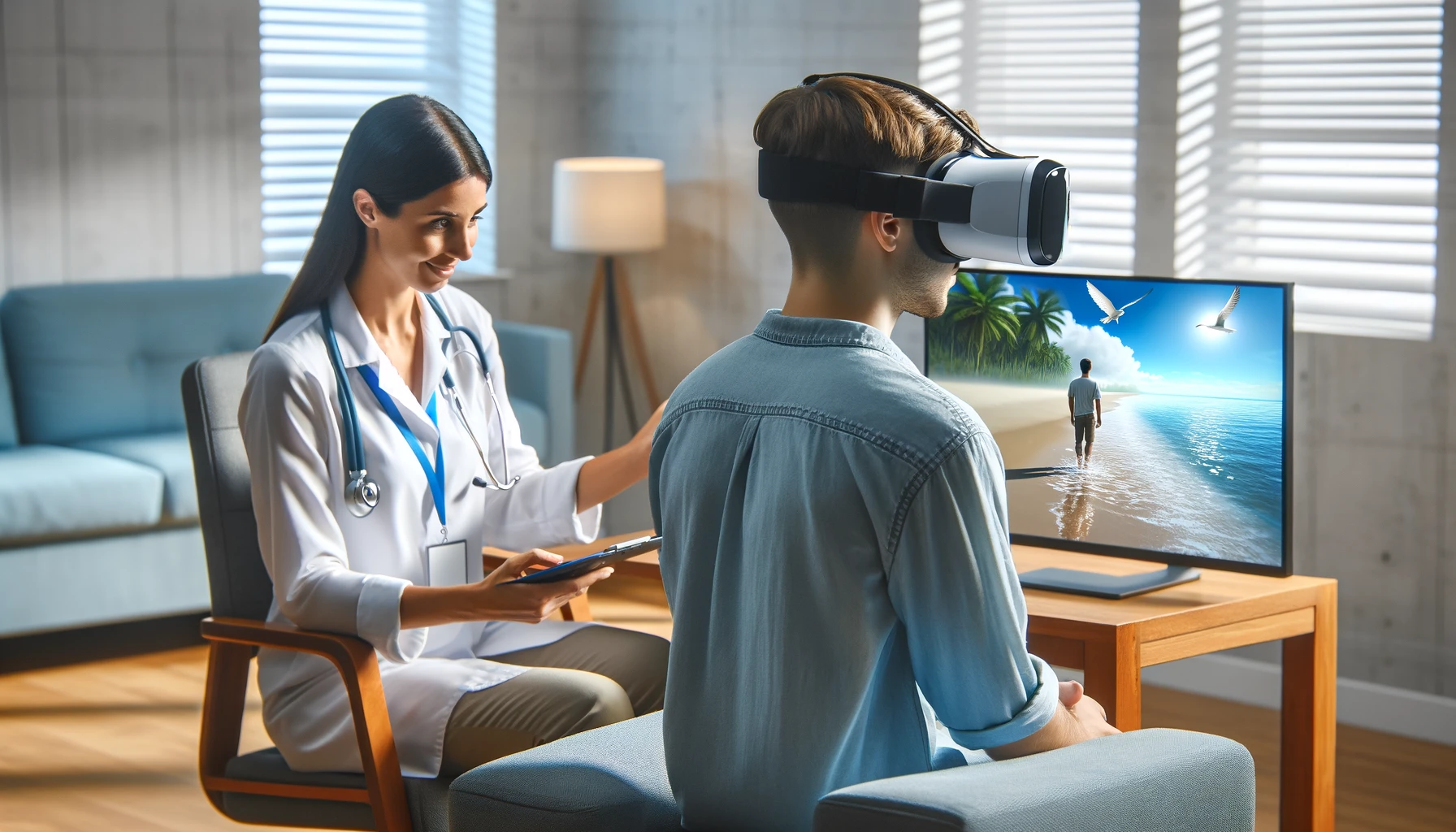


4. Innovative education with XR
XR is setting a new standard in education, making learning more interactive and effective. Using Extended Reality technology, students can visualize abstract concepts and explore academic content dynamically, facilitating deeper understanding and knowledge retention.


5. Retail & Extended Reality
The retail industry is rapidly embracing XR to deliver new shopping experiences. From virtual fitting rooms to 3D product visualizations, Extended Reality is shaping the future of shopping, providing customers with a powerful tool to visualize products in their desired context before making a purchase.
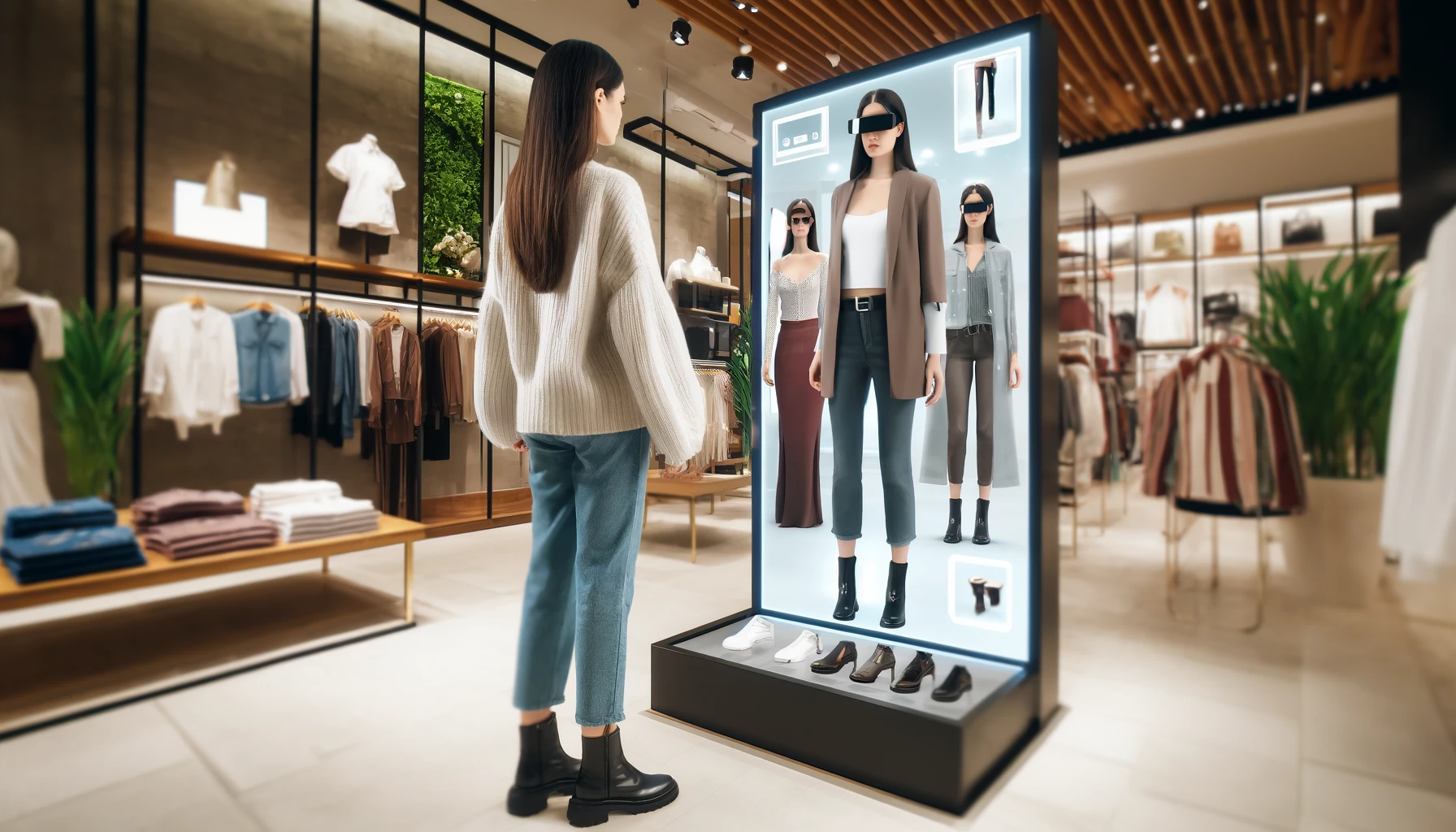
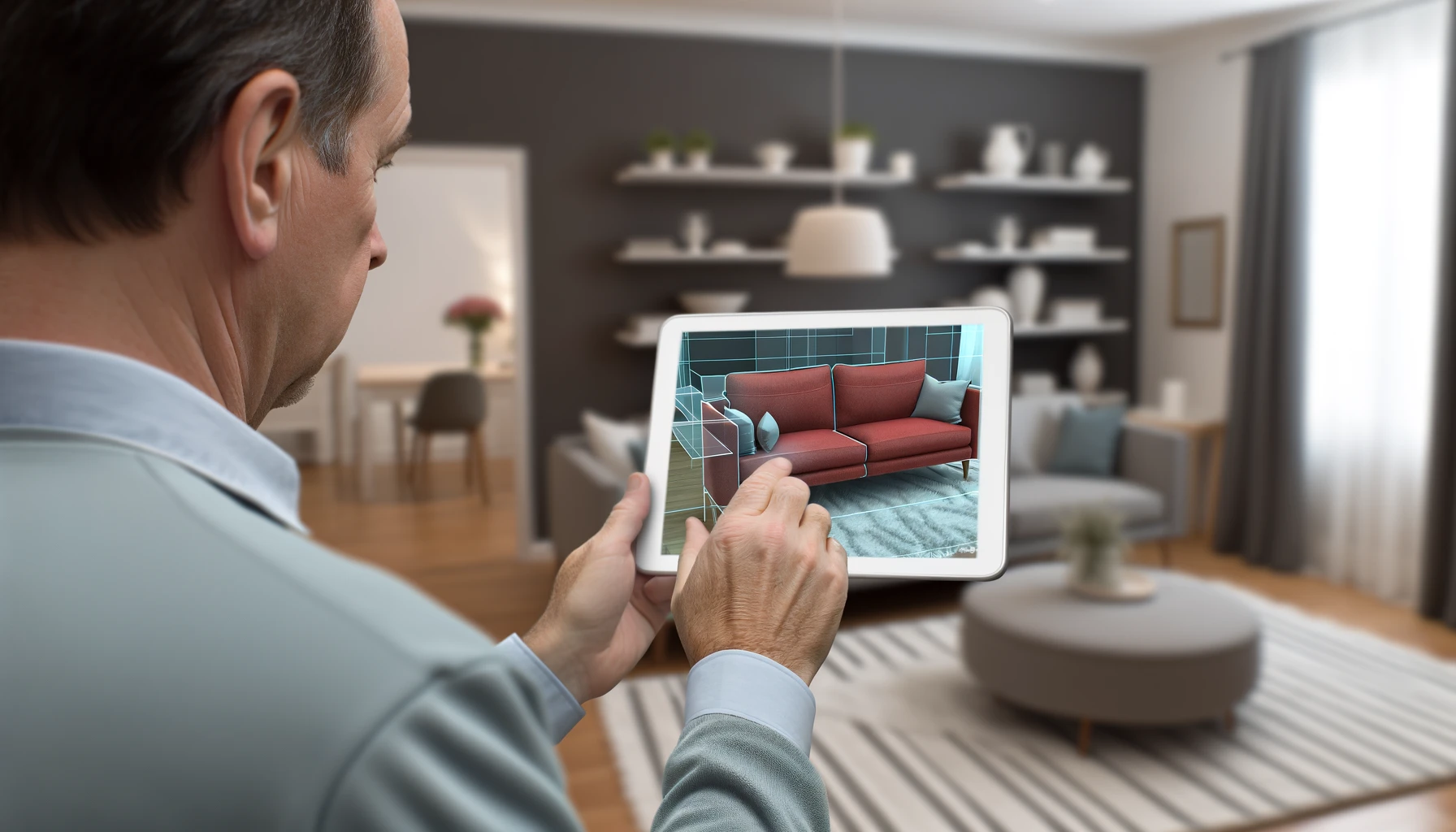


6. Advanced industry with XR
In industry, XR contributes significantly to improving operational and training processes. Through the use of augmented reality, workers can receive detailed visual instructions in real time, improving work accuracy and safety in complex industrial environments.


7. Immersive entertainment with Extended Reality
The entertainment industry has been an early adopter of XR, creating deeply immersive experiences for games, movies and sporting events. Extended Reality enables users to immerse themselves in digital experiences that completely transform the interaction and enjoyment of content.


8. Engineering and Extended Reality
Engineering benefits greatly from the implementation of XR for project design and analysis. Engineers can use XR to visualize 3D structures prior to execution, facilitating more efficient and accurate collaborations in the design of complex projects.


SIMILAR CONTENT












 RETURN
RETURN







